Cold climate heat pumps can meet 100% of your heating needs, without fossil fuel back up. Unlike traditional heating systems that burn fuel to generate heat, a heat pump uses electricity to move heat into or out of a building. This transfer of heat, rather than combustion, means that cold climate heat pumps are a highly efficient way to heat and cool your home.
Unlike burning gas or oil, heat pumps can keep you warm in winter and cool in summer without contributing to climate change.
For an introduction to heat pumps, watch this video!
What is a cold climate air source heat pump?
Cold climate heat pumps can heat efficiently even when temperatures are below freezing.
Heat pumps can transfer heat into your home from air, water, or the ground outside your home. Air-source heat pumps are the most common configuration, with a compressor unit outside connected to either a system of heating/cooling ducts or a single or multiple “ductless” room-sized air handers or “heads,” as in the illustration below.
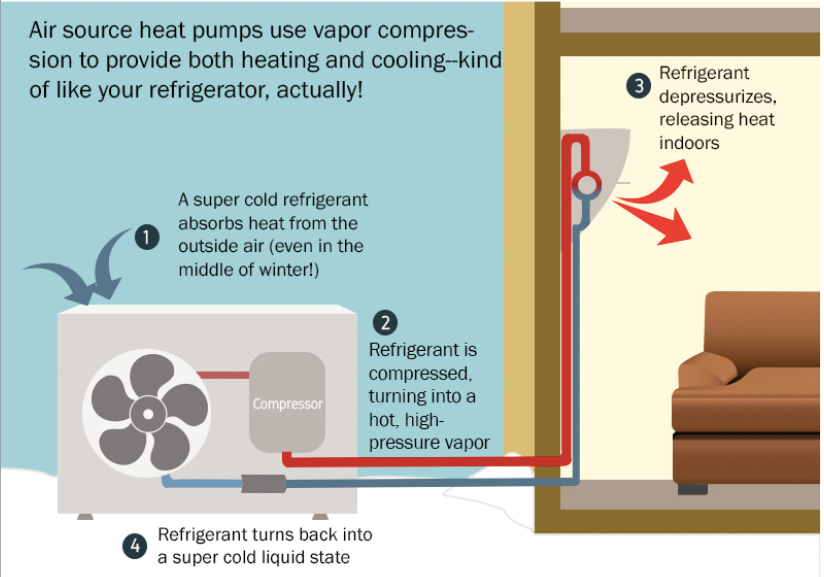
For a more in-depth introduction to how heat pumps work, we recommend this article: A beginner's guide to the different types of heat pumps.
Who should install a heat pump?
Heat pumps benefit some households more than others. Consider a heat pump if you answer yes to any of the following questions. (These questions and more details can be found at https://goclean.masscec.com/clean-energy-solutions/air-source-heat-pumps.)
Do you want to reduce your home’s greenhouse gas emissions?
Do you currently heat your home with oil, propane, or electric resistance?
Are there parts of your home that are not adequately heated or cooled by your existing system?
Do you currently have a hot air heating system (i.e., furnace) that is old or inefficient?
Do you want to add air conditioning to your home?
Do you want to replace your current central air conditioning system?
Do you have an open concept house (large spaces without doors)?
Do you have photovoltaic solar panels on your roof?
Is your house weatherized (i.e., well-insulated and air-sealed)?
Heat pumps run on electricity so, to figure out if one is affordable for you, compare the projected reduction of your current heating fuel to the projected increase in your electricity usage. If you are replacing an older air conditioner, factor in a reduction in kilowatts needed to keep you comfortable in summer.
Rebates and Tax Incentives
Rebates for heat pumps depend on where you live and other factors.
Rhode Island’s Office of Energy Resources launched the CleanHeatRI program in September 2023. Read about new program at: CleanHeatRI. A full list of incentives can be found at: Incentives - Clean Heat Rhode Island (cleanheatri.com)
And in Massachusetts, those who heat with gas now have a greater heat pump incentive through Mass Save. Incentives for switching from oil, propane, and electric resistance are also strong. Read more at Heat Pump Rebates (masssave.com).
Thanks to the Inflation Reduction Act, you may be able to claim a federal tax credit for 30% of your heat pump installation, up to a maximum of $2,000. Federally funded rebates are also coming in late 2024. You can find more information about this through the Rewiring America IRA calculator.
Heat pump benefits
One system for home heating and cooling
Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling through the same system. In homes with more than one indoor head, homeowners can have more precise control over the temperature in various parts of their homes.
Potential energy bill savings
Heat pumps are highly efficient systems and may save homeowners money on their heating bills. Heat pumps will provide significant savings over electric resistance and are likely to be cost-effective compared to propane and oil heat. Heat pumps are a considerably greener technology than gas heat, but they may be more expensive to operate than gas heat. Heat pumps are much more efficient than window air conditioners.
High efficiency, lower emissions
Replacing all or part of your heating needs with a high-efficiency heat pumps will reduce your home's greenhouse gas emissions. Of course, if you green 100% of your electricity through our Green Powered program, then there are no emissions when you use heat pumps!
Quiet systems
If you're used to hearing radiators creak in the winter and using loud window air conditioning units to cool off in the summer, heat pumps will be noticeably quieter.
Air quality and safety
Heat pumps filter and dehumidify air, improving indoor air quality and comfort. Unlike gas, oil, and propane equipment, heat pumps emit no combustion gases, and carry no risk of combustion.
How to get a heat pump
You can research heat pumps, talk with an unbiased expert, or compare quotes side-by-side through the state and municipal heat pump programs and EnergySage. Start at https://info.greenenergyconsumers.org/shopheatpumps to find links appropriate for your location.
Here are more resources on heat pumps:
- General information: Mass Clean Energy Center's "Learn About Air-Source Heat Pumps"
- Rebates in Mass Save territory: Mass Save's Electric Heating and Cooling Equipment
- Rebates in Rhode Island: CleanHeat Rhode Island
Testimonials
-
Ezekiel W.
I had a chat with Abode so I could be informed when working with my installer and getting a 2nd quote for another location. It was a good chat, I got my question answered quickly and efficiently, and it well worth the $100 for the peace of mind.
-
Jerome E.
After installing a whole home heat pump system, we had no trouble heating, even below zero. Haven’t bought oil for a year now. That’s a good feeling.
-
Paul L.
The four Mitsubishi one-to-one air source heat pumps we installed at our daughter's all-electric house have greatly reduced her electricity usage, which is helping her cope with rapidly rising electricity rates. They are quiet, and they even kept her house comfortable when the temperature dropped to -14ºF. We got a tremendous amount of help from the Mass Save program, which provided a $10,000 rebate and a zero percent, 7-year loan for the balance of the cost.
